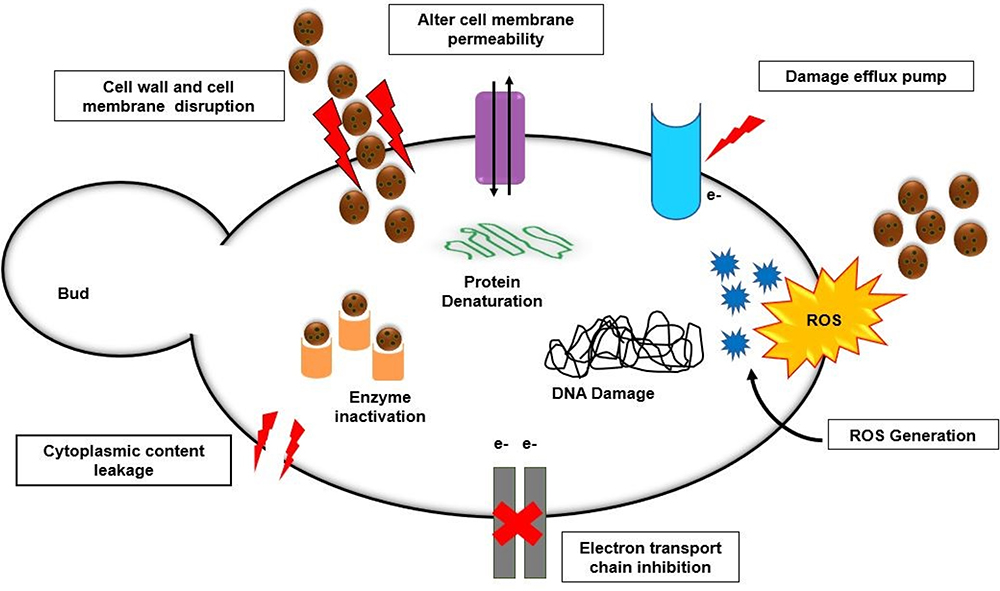
Pharmaceutics | Free Full-Text | Antimicrobial Peptides: Avant-Garde Antifungal Agents to Fight against Medically Important Candida Species

Efficient Capture and T2 Magnetic Resonance Assay of Candida albicans with Inorganic Nanoparticles: Role of Nanoparticle Surface Charge and Fungal Cell Wall | ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering

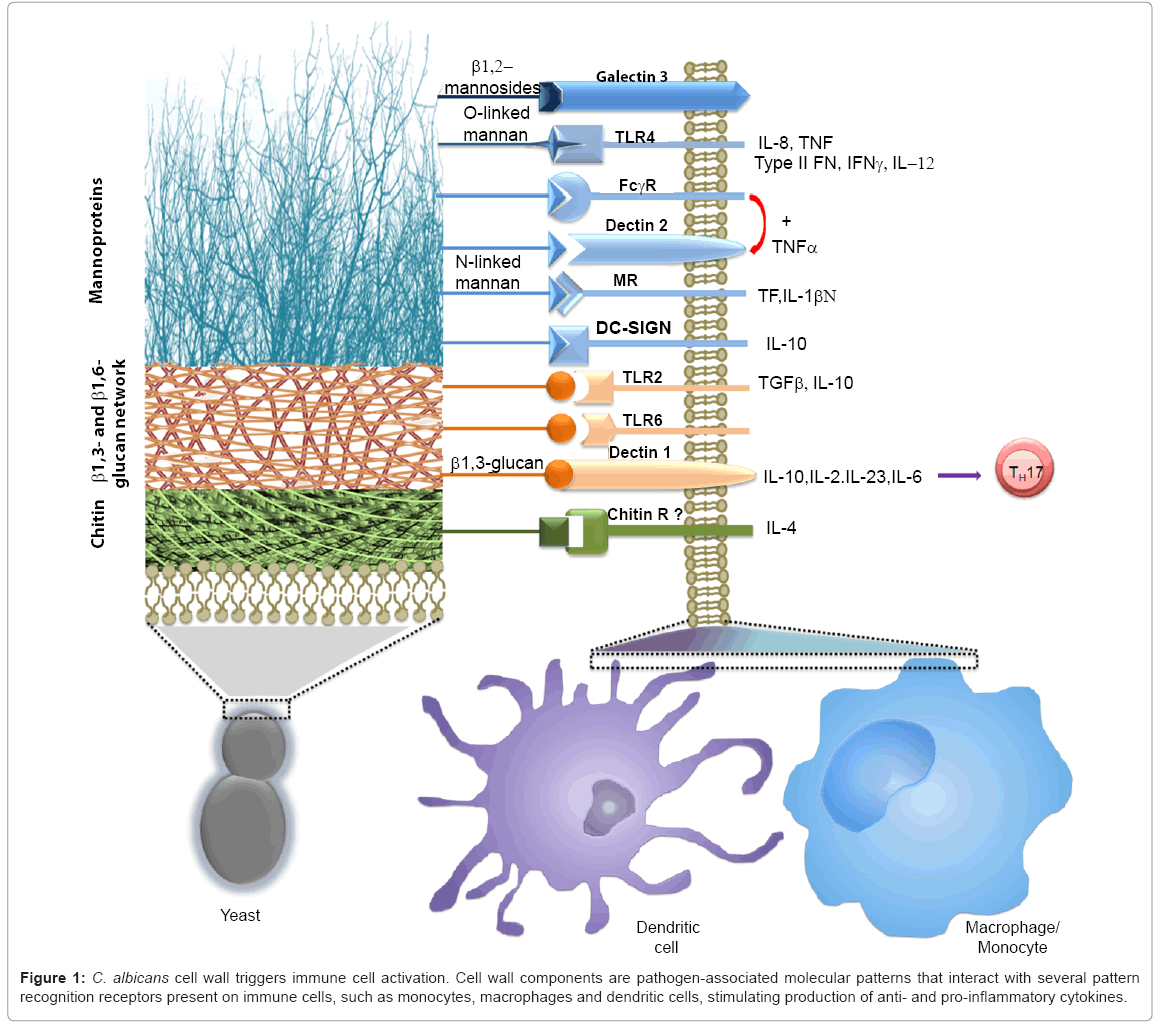
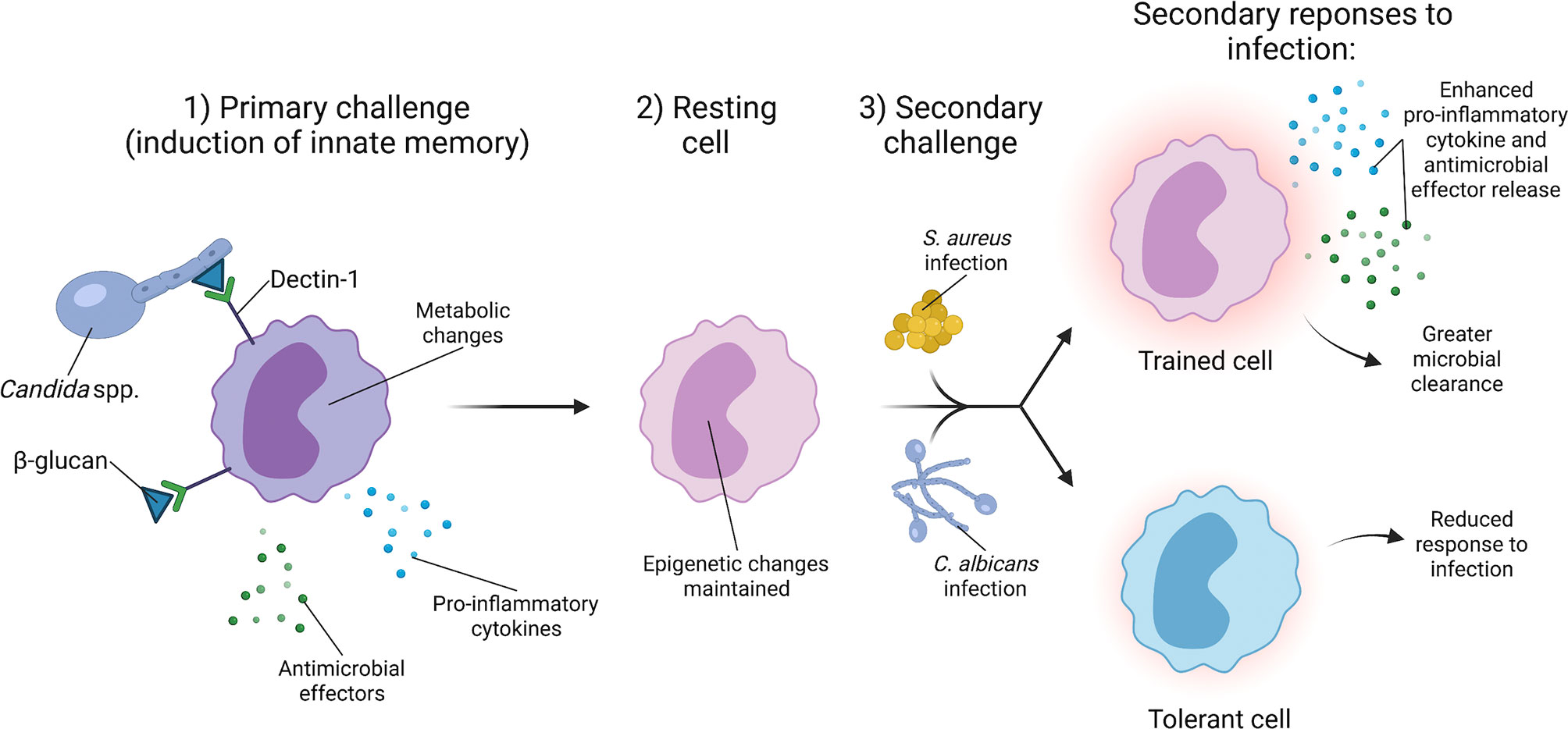
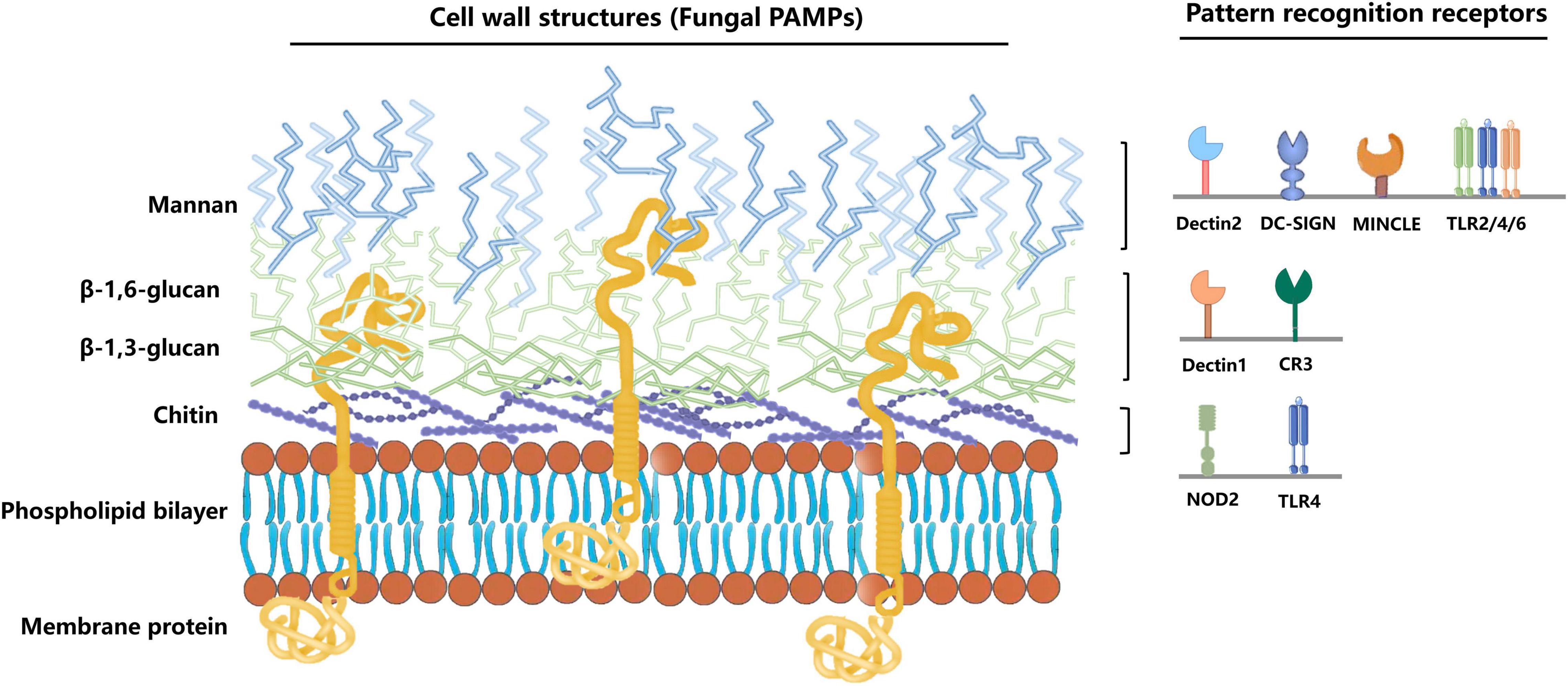
An integrated model of the recognition of Candida albicans by the innate immune system | Nature Reviews Microbiology

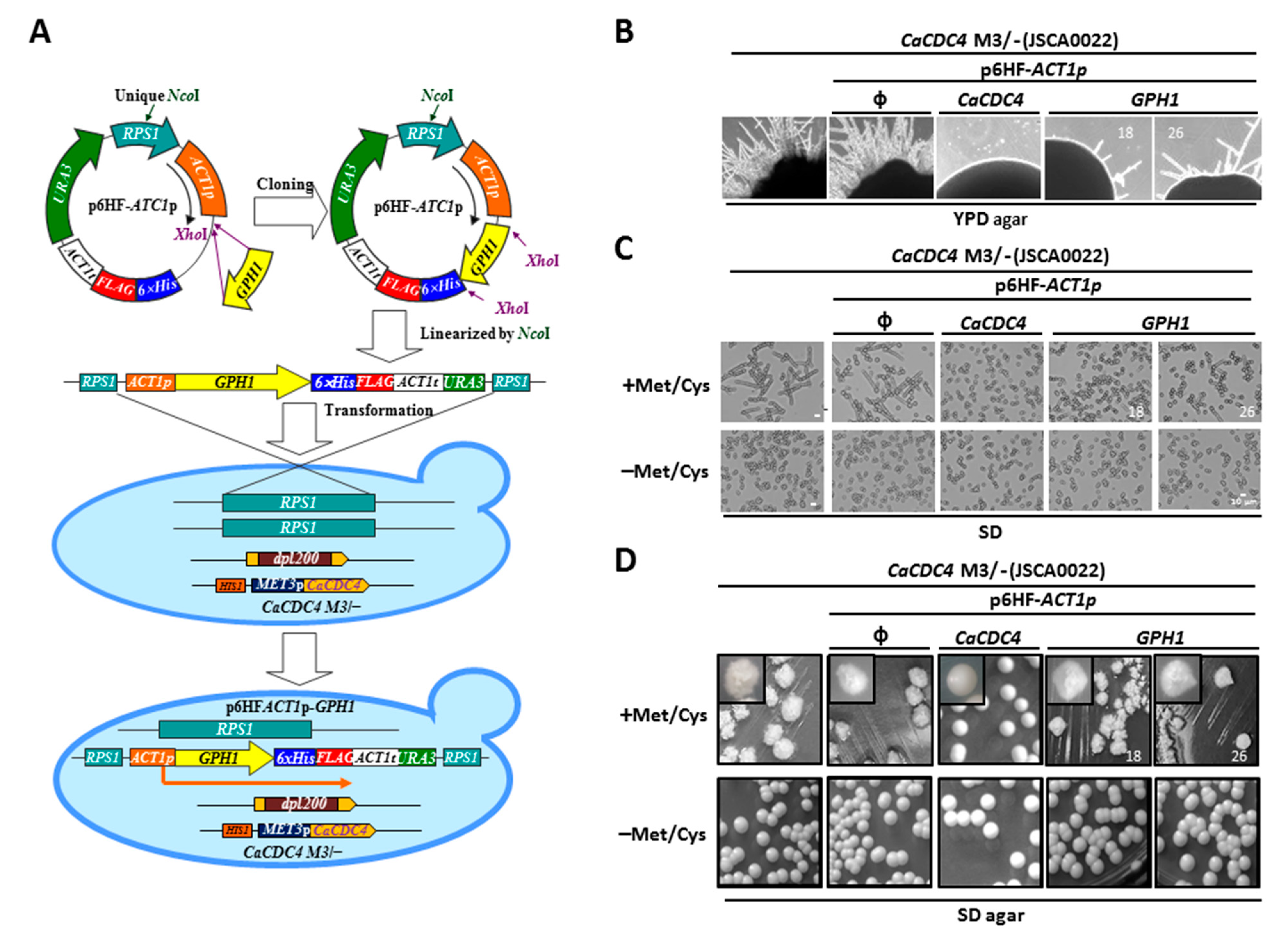
Sec15 links bud site selection to polarised cell growth and exocytosis in Candida albicans | Scientific Reports

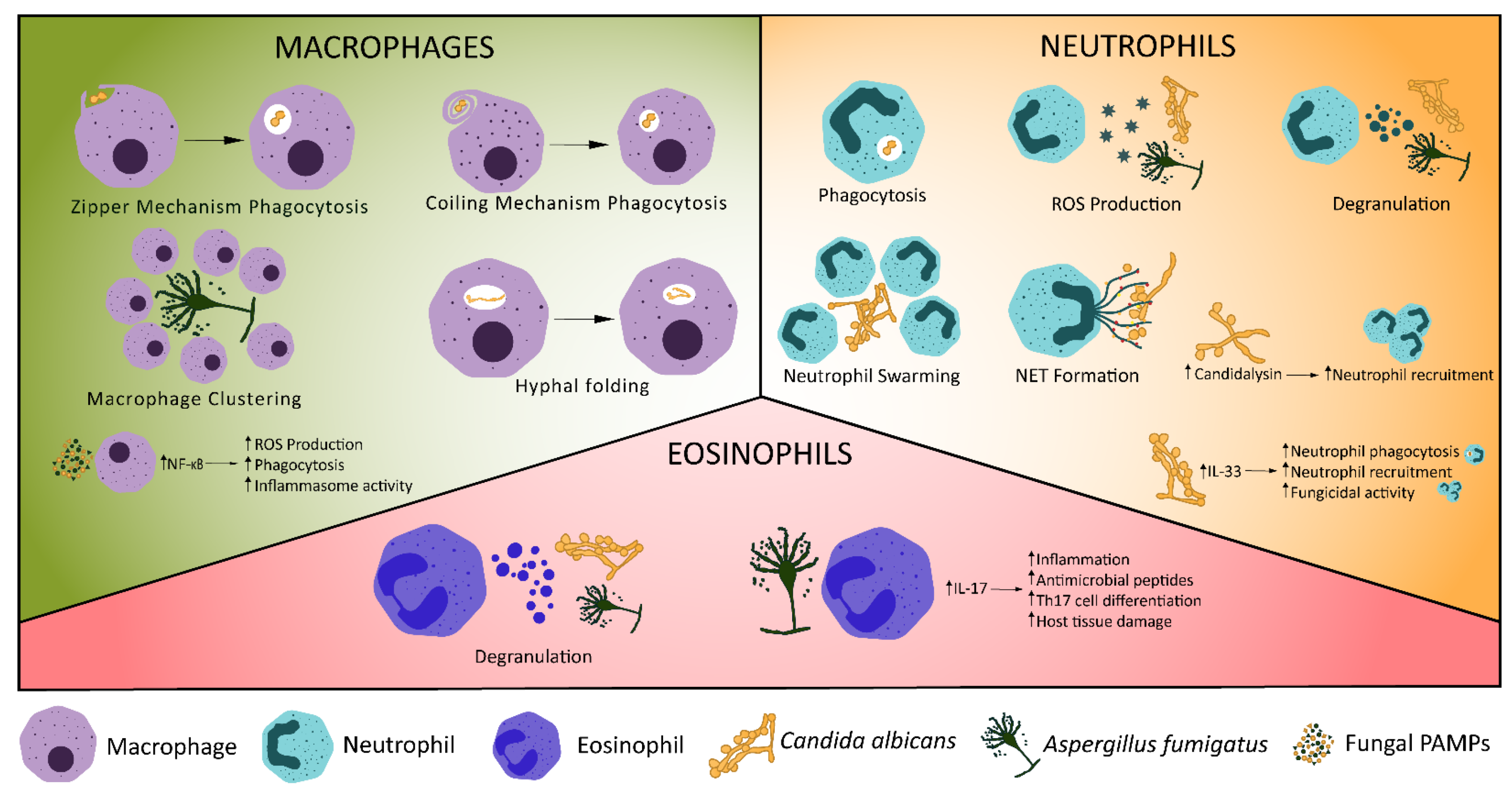
The escape of Candida albicans from macrophages is enabled by the fungal toxin candidalysin and two host cell death pathways - ScienceDirect

Nutrient–fungi–host” tripartite interaction in cancer progression - Wu - iMeta - Wiley Online Library

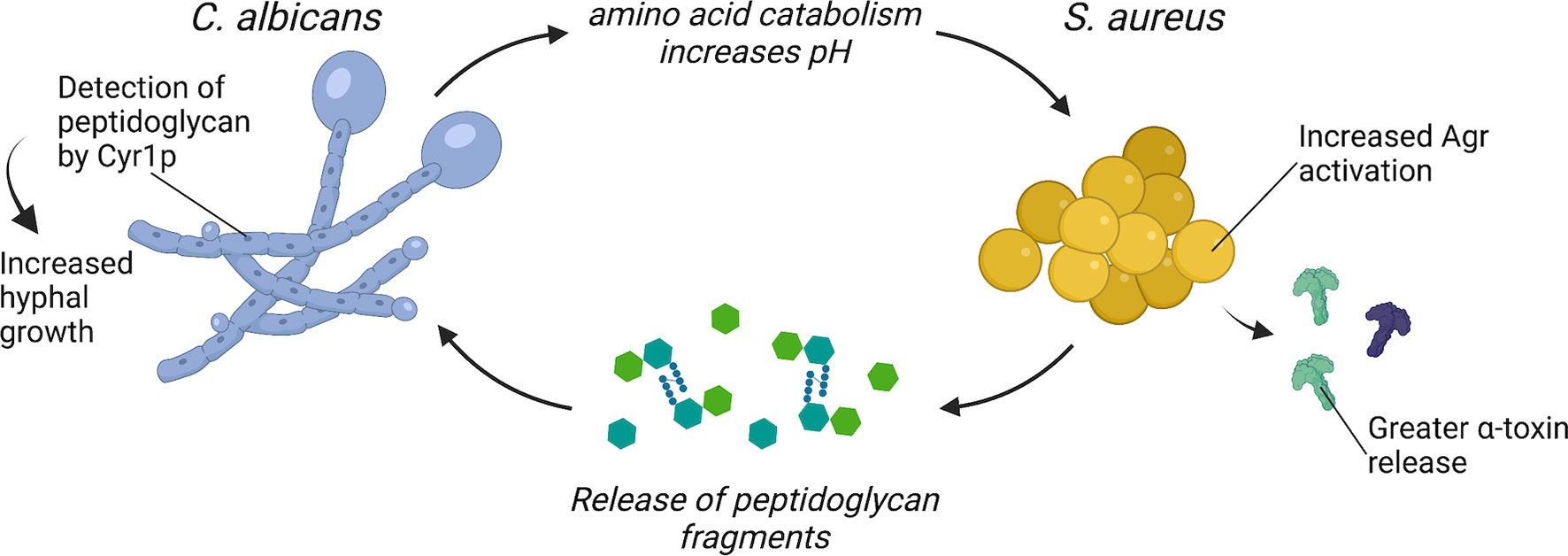
Molecular Docking Reveals Critical Residues in Candida albicans Cyr1 for Peptidoglycan Recognition and Hyphal Growth | ACS Infectious Diseases

Transcriptional responses of Candida glabrata biofilm cells to fluconazole are modulated by the carbon source | npj Biofilms and Microbiomes
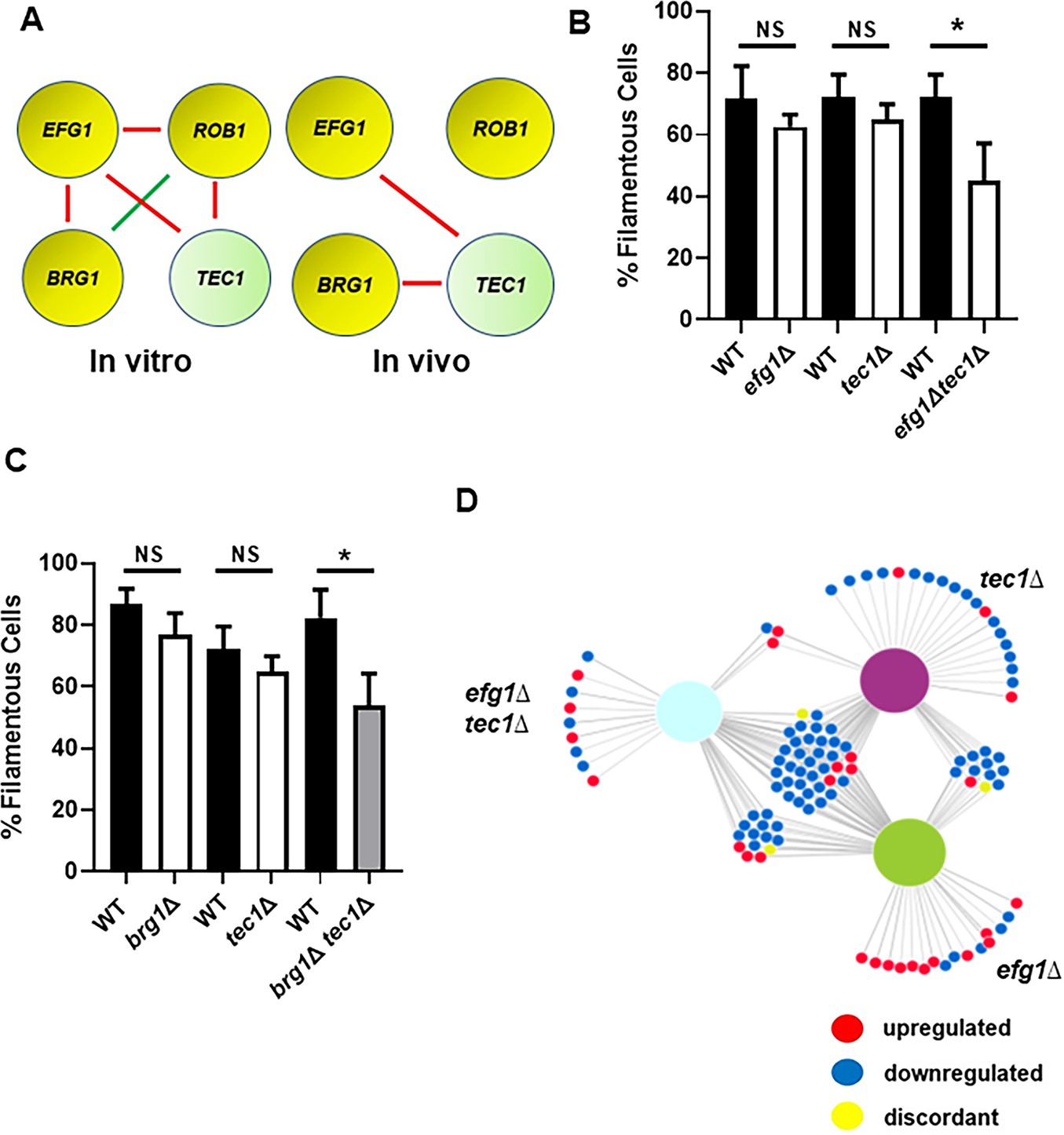
Intravital imaging-based genetic screen reveals the transcriptional network governing Candida albicans filamentation during mammalian infection | eLife

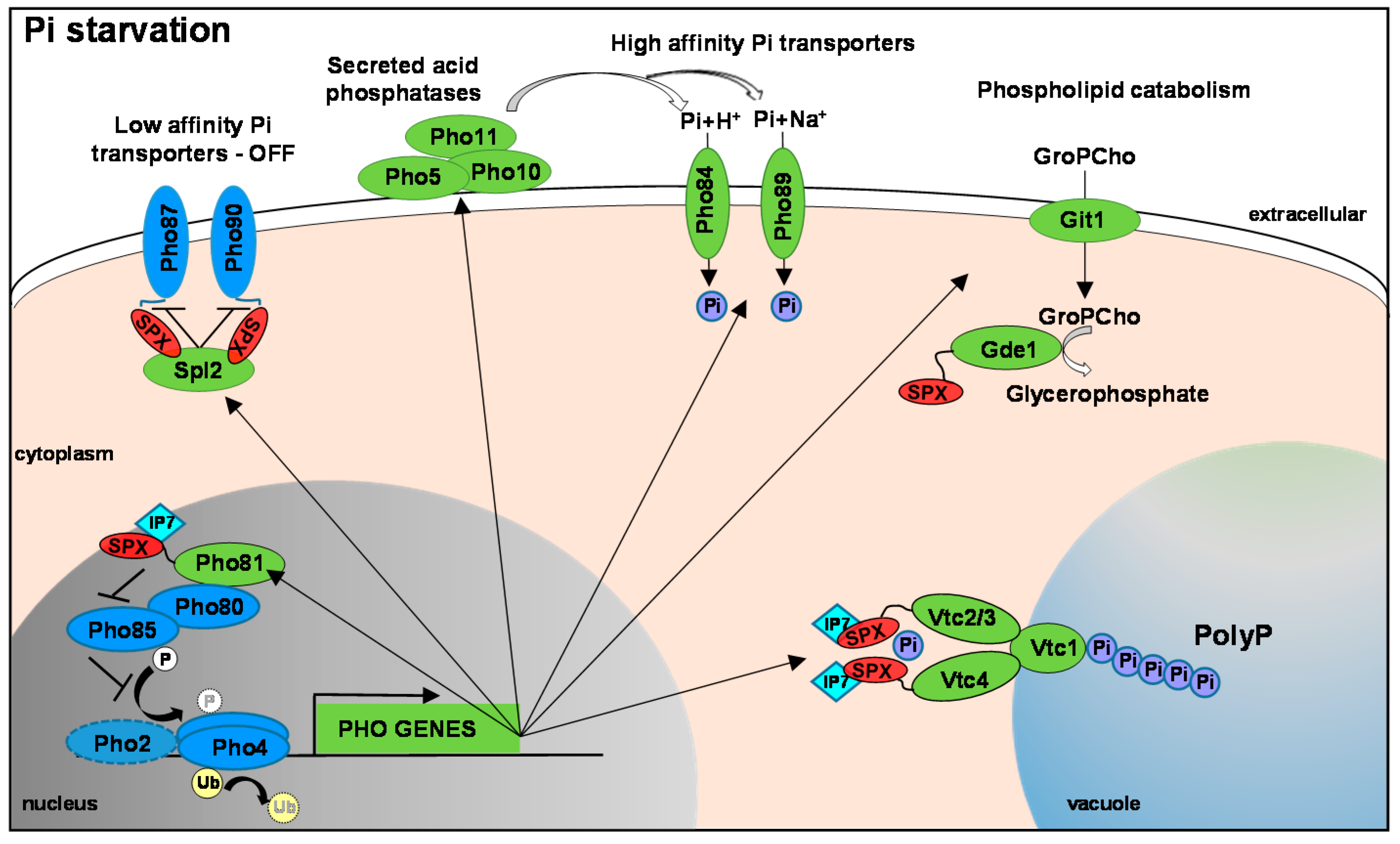
Metabolism impacts upon Candida immunogenicity and pathogenicity at multiple levels: Trends in Microbiology

Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans Ubiquitin and Heat Shock Factor-Type Transcriptional Factors Are Involved in 2-Dodecenoic Acid-Mediated Inhibition of Hyphal Growth

The external face of Candida albicans: A proteomic view of the cell surface and the extracellular environment - ScienceDirect